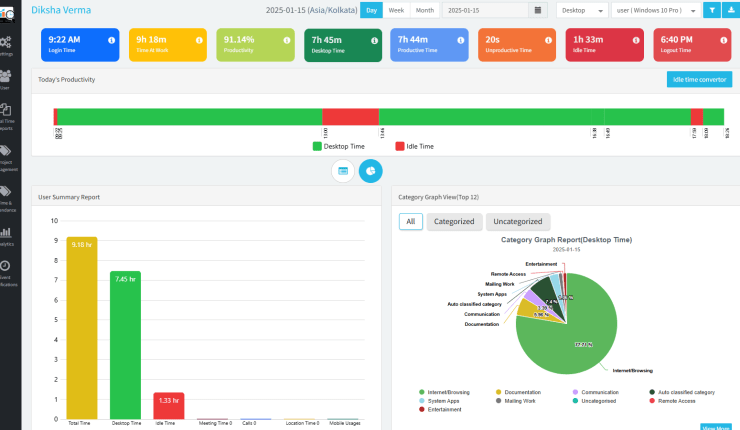
Is time tracking micromanagement? The answer can be yes or no. To summarize, it depends on how you use it in your business. That’s what we will try to decipher in today’s blog. Tracking the work hours of employees has become a big part of team management these days. However, at what cost?
Tracking your employees’ time is good. However, is the investment worth it? You need to consider various factors when implementing software for tracking time. Plus, if your managers are still overdoing it, then it will only be a waste of time. Overall, time tracking is a very complex concept, which we will try to clarify in today’s post.
By the end of this post, you will identify signs time tracking is and isn’t micromanagement. Plus, we will also clarify whether it comes under HR management, provide its other benefits, and also discuss the time-tracking software solution we use. So, let’s get started right away with it.
6 Reasons Why Time Tracking is Micromanagement
![]()
Yes. Although it is not if utilized incorrectly, time tracking can lead to disastrous forms of micromanagement. Now, you must be wondering, how it is possible. Well, there are some cases where tracking your employees’ time can amplify micromanagement.
1. Constant Monitoring
Micromanagers often closely monitor their employees, making them feel nervous. They often check in constantly. What they do is track the progress closely and keep requesting constant updates. Speaking of time tracking software, the advanced ones provide real-time data to your managers. Give this power to micromanagers and they will:
- Use time tracking data to redirect employees’ tasks.
- Interrupt their work with questions about their work-time utilization.
- Request multiple project updates.
2. Lack of Autonomy
Another problem with micromanagement is that employees who have to face it daily have little or no economy when it comes to decision-making or task execution. Moreover, that leaves no room for creativity and innovation as the manager dictates even the most minor details on how to do work. So give them the power of time tracking and you already know how will they negatively impact your employees with it.
3. Limited Trust
Micromanagers often oversee every step of the process. This is due to the lack of trust in their employees. If you think this is bad, then let me tell you that micromanagers will use work-time utilization reports to pit your employees against each other. Instead, they should be encouraging them to learn from each other.
4. Excessive Control
Micromanagers think that their methods and processes are the best. They often suggest particular approaches to handling tasks and projects with no regard for employee suggestions and/or ideas. Similarly, they would want the same, when it comes to tracking time with software such as DeskTrack.
Read Also: How Time Tracking Software for Students Improve Study Habits
5. Ineffective Use
It’s a proven fact that micromanagement is a double-edged sword. Why? You ask. It’s because it leads to inefficient use of work-time for both managers and employees. We all know constant supervision is time-consuming and will decrease productivity. Micromanagers will:
- Use work-time utilization reports to review employees’ work or challenge their project and task management approach.
- Constantly interrupt employees with data from time tracking software, leading to projects being completed in more time than expected.
6. Demotivation
Micromanagers can and will make their employees feel demotivated, disengaged, and frustrated. Even when using time tracking software, they will get on the nerves of their employees, constantly interrupting them due to a lack of trust.
So now we know how time tracking and the software for it can be harmful when used improperly overused, and/or used by micromanagers.
What you need to do is look for signs of micromanagement and how your managers manage teams. Especially, the former as it is unfavourable for both teams and individual performances. If your managers introduce time tracking tools for micromanagement, then it will:
- Stop creativity
- Obstruct problem-solving
- Make a hostile work environment
Overall, you need to understand the long-term damage from micromanagement and watch out for the time tracking red flags we mentioned above before implementing time tracking software.
5 Signs When Time Tracking is Not Micromanagement
![]()
Now we know how time tracking can be micromanagement. However, primarily, it is not. If the implementation is correct, then this aspect of team management can have many benefits. But first, let’s look at the 5 signs indicating that time tracking is not micromanagement.
1. Empowerment
Time tracking can be the best way to empower your employees when you focus on outcomes and work quality rather than the processes. The bottomline is that you need to use the work-time utilization reports to show your employees how their focus is providing you with results for the most crucial tasks and projects.
2. Flexibility
Proper time tracking gives full control to the employees when it comes to selecting the approach to manage projects and tasks. Both employees and managers receive real-time insights into the effort they require to finish tasks, work status, and other insights including:
- A recommended approach to complete a task.
- Your employees and teams can learn from and apply to future projects.
3. Efficiency
Properly tracking your, your managers, and your employees’ time ensures that you easily spot work-time gaps such as:
- Excessive meetings
- Review sessions
- Other unproductive events that hinder the workflow.
Read Also: Top 10 Time Tracking Software in the Philippines for 2025
4. Motivation
Properly tracking your and your employees’ time also motivates you all to keep working harder and smarter. This is so because everyone can see their contribution to the success of your business by seeing a direct line between:
- Their efforts
- Your organization’s success
5. When Done the Right Way
Time tracking software when done the right way can benefit you and your business in many ways. By following all the rules and being compliant with the labour laws and regulations, you, your employees, and your organization can gain the fruits of:
- Increased employee efficiency
- Productivity boosts (to the point of maximum)
- Reduced expenses
- Timely project completions
- Improved employee time management
- Maximum profitability
5 Other Benefits of Time Tracking

So now we know that time tracking is not micromanagement when properly implemented and utilized. Moreover, there are also some long-term benefits of utilizing the right time tracking software. We shortlisted the 5 of them for you to understand the power of properly utilising time tracking software.
1. Better Project Planning
Did you know that according to a survey by Deloitte, 91% of employees say that having unmanageable stress and frustration negatively impacts work quality? 77% of employees have experienced burnout with half of them having experienced it more than once.
That’s because project planning is very complex. Even the most experienced leaders face challenges in planning for optimal resource usage and employee scheduling without overburdening teams. In short, it is one of the most stressful elements of project management. So project managers use time tracking to:
- Help team members take advantage of their highest valued skills and capabilities where and when it matters the most.
- It helps reduce stress and burnout, which increases the chances of meeting quality deliverables and project objectives.
- Plan for future projects by using lessons learned from work-time utilization reports to address mistakes, helping teams improve work performance.
2. Improved Team Productivity
Tracking and improving employee productivity is essential for the success of your projects. For example, on average, employees attend 11-15 weekly meetings. It is higher than the bar for project teams. Plus, to make it worse, not all of them accomplish something. Long story short, you can’t know that meeting time is spent well or have meaningful conversations without time tracking.
Another alarming statistic is that 35% of team members feel that at least 5 hours of weekly meetings are a waste of time and expenses (from business POV). On the other hand, tracking time lets you isolate and decrease:
- Rework
- Errors
- Team fatigue
3. Setting Clear Expectations
Time tracking involves more than just tracking the total hours your employees have been working for you over the years. You need to get a 360-degree view of how your teams are utilizing their time. Doing so lets you prioritize and communicate task-related concerns and information.
According to a Gallup study on employee engagement, setting clear expectations increases up to 10% productivity and decreases turnover by up to 22%. So, to summarize, you need to set clear expectations to increase team buy-in and engagement through time tracking data. This ensures more productive teams due to exceptional timely results delivery.
Read Also: Top 15 Employee Scheduling Software for Businesses in 2025
4. Risk Management
Assessing risks and how your teams effectively manage time, resources, and project budget depends on project time tracking, enabling you to answer questions including:
- Is the project on track?
- Is your project over budget?
- Which resources are available and where?
- How much has been used and required?
- Where has the most time been spent?
Overall, project managers use time tracking data to:
- Evaluate the progress of the project.
- Answer tough questions
- See where the project can falter
- Get more time to make the necessary changes for optimal risk mitigation.
5. More Profitability
You already know that time is money. This line is more accrued when it comes to project management. It is because, here, you need to balance time and budget precisely to meet project objectives. You see that all projects must provide you with some value in any form. Mostly, you would want financial benefits.
The vitality is to track actual time vs budgeted time as it helps you understand resourcing, burn rates, and projected project financial gain or loss. Overall, time tracking ensures that your project managers can accurately estimate, budget, and track costs adjustably as per requirements to remain more profitable.
Does Time Tracking Come Under HR Management?
So whether time tracking comes under HR management or not depends on the type of your business.
For example, if you employ people on hourly contracts, then it makes sense for your HR teams to manage time tracking as they might be responsible for payroll.
To accomplish this, organizations usually use employee scheduling software, shift management, and timesheet software.
However, if your employees are salaried and work fixed weekly hours, then time tracking won’t come under HR management.
Overall, if the collected data doesn’t impact employee pay or client billing, then, there is no need for your HR to use time tracking.
Choose DeskTrack: The Better Time Tracking Software
DeskTrack is the best time tracking software, which 10s and 1000s of organizations worldwide use. Although other software solutions also provide similar features and functionalities, the reason we use this tool is because of the real-time functionality. I.e., real-time time and activity tracking, real-time reporting, and real-time project progress tracking.
Other than simple time tracking, DeskTrack also provides you with more features and functionalities for project management, employee monitoring, productivity tracking, employee scheduling and more. To summarize, it’s the only tool you will ever need to streamline work performance.
Conclusion
So now we have finally answered the question, is time tracking micromanagement? It is not. However, it can be if you use work hours tracking and the software for it improperly. It’s even worse if it’s done by a micromanager who manages everything themselves, leaving little to no room for employee creativity, feedback, ideas, and/or suggestions. On the other hand, if you use it in the right way by following all the rules, laws, and regulations, it can empower your employees by flexibly motivating them to improve efficiency. However, there are also some long-term benefits of using time tracking software such as DeskTrack, which accrue and makes efficient everything related to project management and makes your business more profitable than ever.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q.1 Is Time Tracking Another Task Added To Your Daily Work?
Ans. In a way, yes. If you think from a broad perspective, you won’t get any useful insights unless you track everything that you do and don’t do. This adds starting/stopping task timers as another mandatory work in your list. Failing to do that can be frustrating in the long run.
Q.2 Isn’t Time Tracking a Form of Micromanagement?
Ans. Time tracking has never been micromanagement and will never be. However, it can be if you use it improperly. For instance, if you are tracking employee attendance, your employees must clock in and out on time for correct payroll and salaries. If you are tracking desk employees’ time, recording desktops to an extent is good. However, it should not exceed limitations. Similarly, tracking long-term activities is for knowing where your employees are deployed and is essential for management.
Q.3 What are Some Instances of Time Tracking Being Micromanagement?
Ans. Here are some examples of time tracking being micromanagement.
- Constant Monitoring
- Lack of Autonomy
- Limited Trust
- Excessive Control
- Ineffective Use
- Demotivation
Q.4 When is Time Tracking Not Micromanagement?
Ans. Below, we have listed the 5 signs indicating that you are properly using time tracking software.
- Empowerment
- Flexibility
- Efficiency
- Motivation
- When Done the Right Way
Q.5 What are the Other Benefits of Time Tracking?
Ans. Utilizing time tracking software has other benefits in project management including:
- Better Project Planning
- Improved Team Productivity
- Setting Clear Expectations
- Better Risk Management
- More Profitability