Overtime can be one of the highest bearable costs for any business. The FLSA regulates this pay at 1.5 times an employee’s regular rate of pay. This may not look like much. However, it can quickly stack up. Furthermore, according to the Fair Labor Standards Act in the USA, you are also required to maintain proper records of employee hours, as failing to do so can render you legally liable. However, no need to be afraid. In this blog, we will reveal the most efficient way to calculate overtime pay accurately.
What Is Overtime?
Overtime is when any employee works over the standard 40-hour workweek. As we mentioned before, according to the FLSA, you must pay overtime at 1.5 times the regular hourly pay rate of the worker. For example, if X worked 5 hours more at $10/hour, then he would get $10 * 1.5 = $15/hour for the extra time. That’s a standard rule. However, you also need to remember a few more things.
- Exempt employees usually don’t get paid for overtime.
- Double time or double overtime is when employees get paid double their regular pay rate. According to our example, $10 * 2 = $20/hour.
- There are also custom overtime pay rates, which employers may negotiate in contracts or may vary by industry. For example, 1.75, 1.6, 1.8, etc. However, it can’t be lower than 1.5.
- California, Nevada, Alaska, Colorado, and Oregon are among the only US states that mandate daily overtime and double time pay calculations. Among these, California is the only US state with actual double time laws.
Read Also: Will Artificial Intelligence Ever Replace Human Intelligence?
Types of Overtime
So, how is overtime calculated? Believe it or not, to answer this question properly, you need to know about the different types of overtime. Simply put, the calculations slightly vary. However, to make it simple, you can use a free overtime pay calculator. Who knew that a thing as simple as overtime would also have categories.
1. Hourly
It’s simple to calculate overtime for hourly employees. All you must know is their hourly pay rate, their total hours, and their overtime pay rate. Here’s an example of our employee X:
- First, we will calculate their base pay: $10/hour * 40 = $400
- Now, it’s time to calculate the overtime pay rate for X: $10/hour * 1.5 = $15/hour
- We will now multiply their overtime rate by their overtime hours: $15/hour * 5 = $75
- We will add what we just got to X’s base pay to get their total pay = $400 + $75 = $475
2. Salaried
You must also pay salaried or non-exempt employees overtime at a minimum of 1.5 times their regular pay. Here’s how to calculate overtime for X in this scenario.
- Let’s say X has an annual salary of $20800. We will calculate their weekly pay by dividing this by 52: $20800/52 = $400.
- Next, we will get X’s regular hourly pay: $400/40 = $10/hour
- Now, it’s time to calculate the overtime pay rate for X: $10 * 1.5 = $15/hour
- We will now multiply their overtime rate by their overtime hours: $15/hour * 5 = 75
- We will add what we just got to X’s base pay to get their total pay = $400 + $75 = $475
3. Variable Pay Rate
We will calculate overtime pay like this if you have employees at variable pay rates for different jobs or roles. For example, differential pay shifts, prevailing wage jobs, etc. In such cases, the FLSA instructs businesses to take the weighted average of all pay rates and divide them by the total work hours at each role. Moreover, weighted overtime is also called blended overtime. Let’s make it clearer with an example for our employee Y this time.
- Let’s say Y swapped shifts with X for 5 hours and earned another $10/hour. Plus, his regular pay rate is also, let’s say $10/hour at 40 hours to keep our calculations simple. That’s $10 * 5 = $50. Likewise, he earns another $10/hour * 40 = $400, making it $450.
- Now we will divide what we got by the total work hours to get the weighted average regular rate: $450/45 = $10
- Now we need the time and a half pay. For that, we will get the half-time by multiplying the weighted average regular rate by 0.5: $10 * 0.5 = $5
- The next step is simple. All we have to do is multiply what we get by the total overtime hours: $5 * 5 = $25
- To get Y’s total pay, we will add their half-time pay to their total straight time earnings: = $25 + $450 = $475
4. Piece-Rate
When you pay your employees for the number of goods they produce or the services they complete, it will be a piece rate for their output. Like your regular workers, you also must compensate these staff members for overtime. Let’s take an example of another one of our fake hard-working employees, Z.
- For example, Z worked for 50 hours, earning $500. Their per-hour pay rate will be: $500/50 = $10/hour.
- Since we already know that the above also includes their straight-time earnings, we will just divide $10 by 0.5 to get their half-time pay: $10/0.5 = $5
- Next, we will divide what we get by their total overtime hours = $5 * 10 = $50.
- For the total payment due, we will add this to what we got in step 1: $500 + $50 = $550
| DeskTrack Fact |
| If the above is too confusing, the FLSA also allows you to pay overtime to piece-rate employees for every, let’s say, shirt produced. This must be at least 1.5 times. However, this must be enough to cover the minimum hourly wages. |
5. Tip-Based
So, how to calculate overtime for tip or commission-based staff members? Something known as tip credit comes into play here. You can claim up to $5.12 to pay employees towards the minimum wage here. However, remember that the amount you claim will significantly affect your extra hours calculations. In this example, Z is now a waiter who gets tips too.
- Let’s say Z got $10/hour in cash for working 50 hours. Here, we will use the full tip credit at $7.25. For overtime, multiply this by 1.5: $7.25 * 1.5 = $10.88
- Now, we will subtract the tip credit we claimed from the overtime rate: $10.88 – $5.12 = $5.76. That’s their adjusted overtime rate.
- You know the drill already, that now we will multiply what we get by Z’s total overtime hours: $5.76 * 10 = $57.60
- To obtain Z’s total pay, we will multiply their overtime pay by their straight pay: 40 * $10 = $400
- For their total payment due, we will add their regular and overtime pay = $400 + $57.60 = $457.60
| DeskTrack Fact 2 |
| You must also not forget that Z must also receive $5.12 * 50 = $256 in tips. This is to meet the federal minimum wage, so that you can apply for tip credit according to the FLSA regulations. |
6. Bonus-Commission-Based
Some employees also get bonuses or commissions other than their regular hourly wages. According to the FLSA, USA, there are strict rules on whether commission-based employees are exempt or non-exempt from overtime pay. Here’s a breakdown.
- Discretionary Bonuses: Since your employees can’t expect to receive this from you, you don’t have to worry about accounting for discretionary bonuses. Simply put, it’s totally up to you whether you want to pay this additional money to your workers or not.
- Nondiscretionary Bonuses: You don’t have to account for this as well when calculating overtime pay. However, your employees will receive this sum as part of their wages or salaries. For example, sales commissions.
First, we will determine whether the bonus paid to Z was discretionary or not. If it were nondiscretionary, we would consider it while calculating their overtime pay. Here’s an example with Z as a life insurance seller now.
- The hard-working employee still earns $10/hour for working 50 hours. Thankfully, they earned $10 as a commission for selling your top plan. Firstly, we will multiply Z’s regular hourly rate of pay by the hours worked. Don’t forget to add their commission: ($10/hour * 50) + $10 = $510.
- We will now divide this by Z’s total hours worked: $510/50 = $10.2
- We will now multiply this by 0.5 to get the half-time in their time and a half: $10.2/0.5 = $5.1
- We will now multiply what we got in step 3 by the total overtime hours of Z. $5.1 * 10 = $51.
- Now, we will add the totals we got in steps 1 and 4 to get the final total. We mean total payment due for Z: $51 + $510 = $561.
How to Calculate Overtime Pay
So, how to calculate overtime in general? Here’s a revision of how it conventionally works.
- Overtime rate is at least 1.5 times for every hour an employee works over the standard FLSA 40 hours/week. However, it can also be any amount based on the contract. For example, 1.75 times.
- Sticking to 1.5, let’s say X worked 2 hours over 40 at $10/hour. Their regular weekly pay will be: $10/hour * 40 = $400. Similarly, the overtime pay will be: $10/hour * 1.5 = $15/hour
- For overtime pay, we will simply multiply the overtime rate by their overtime hours: $15/hour * 2 = $30.
- So, their total payment for the week will be: $30 + $400 = $430.
| DeskTrack Fact 3 |
| Did you know that California is among the only US states that mandate daily overtime and double time pay calculations? For example. Let’s say during the 40-hour workweek, which is 8 hours/day for 5 days, X worked 2 hours overtime each for 2 days and 8 hours for 3 days. At $10/hour, their regular pay will be $10/hour *8 * 5 = $400. Now, for their overtime pay, it will be $10/hour * 1.5 * 2 * 2 = $60. So their total pay for the week will be $400 + $60 = $460 |
See, how complicated it is. That was for just one employee. Imagine you have to do this for 10 employees with different overtime rates each, according to their contracts. Plus, you might also have to handle more than 1 type of overtime. It will consume your HRs valuable work hours to calculate overtime. Plus, don’t forget that your HRs are humans after all and can make unintentional, costly mistakes. So, to flip it around and save time, effort, and costs, use time tracking software to accurately record all work hours. Even better if you integrate it with your payroll software. What it does is generate all regular and overtime pay values for all your employees within seconds in real-time or with a click of a button.
Common Mistakes in Overtime Calculation

Other than the mistakes due to the complexities when calculating overtime, there are a few other common mistakes too, when you calculate overtime. Here’s what you need to avoid.
1. Refusing to Pay Unauthorized Overtime
You must pay overtime to all eligible employees. This is regardless of whether you authorized those overtime hours or not. Simply put, the FLSA mandates every employer to compensate their employees monetarily for working overtime hours. Non-compliance can result in severe penalties.
2. Misclassifying Employees
This happens when you are not using the right payroll software. Manually, it is very easy to get lost in multiple things and misclassify employees by mistake. This results in paying the wrong overtime amount or mixing it all up and paying overtime to exempt employees. This is a costly mistake, which results in loss of human resources due to distrust and dissatisfaction. Plus, the FLSA can also penalize you for denying overtime payment.
3. Not Counting All Work Hours
The FLSA mandates you to log all work hours of your employees. According to the law, it is your responsibility as the business owner. However, it is also a good practice to follow. Simply put, you must compensate your employees for all hours worked and not just additional hours.
4. Calculating Overtime Based on Hourly Rates Only
Assuming that the hourly rate is the regular rate of pay for employees is a grave mistake. You also need to consider other factors when you calculate overtime, such as bonuses and multiple shifts.
5. Improperly Using the Fluctuating Workweek Method
You also need to follow some guidelines when implementing what the FLSA denotes as the fluctuating workweek. This is when employee hours vary from week to week. The US Department of Labor highlights these rules for calculating overtime pay.
- Overtime pay is based on the average hourly rate multiplied by the actual work hours.
- You can only use this method if you and your employees agree on a set salary compensation for the weekly work hours, regardless of how many hours they work.
- Their work hours must also change every week.
6. Neglecting State Laws
While calculating overtime, complying with state laws is also mandatory under the FLSA. Failing to do so will result in penalties and even lawsuits. For example, if you have a branch in California and Arizona, the Californian branch must implement daily overtime calculations while the Arizonian branch must follow the over-40-hour overtime rule.
7. Calculating Overtime Manually
If you are still calculating overtime manually, then it’s a costly mistake. You have no idea how many valuable work hours you could have saved by implementing scheduling, attendance management, time tracking, and payroll software.
Read Also: Top 10 Team Collaboration Tools for Remote Teams in 2026
Best Tools to Calculate Overtime Automatically
Other than using the overtime calculator, you can also use other tools to calculate overtime automatically. In fact, these tools are more efficient, feature-rich, and accurate.
- DeskTrack
- Buddy Punch
- Clockify
- Rize
1. DeskTrack
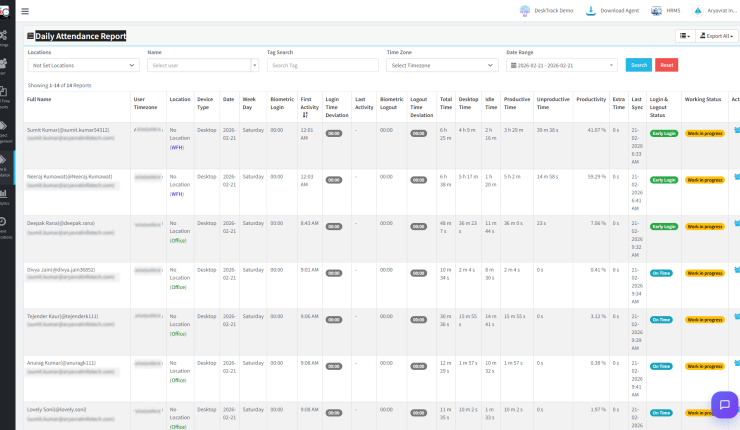
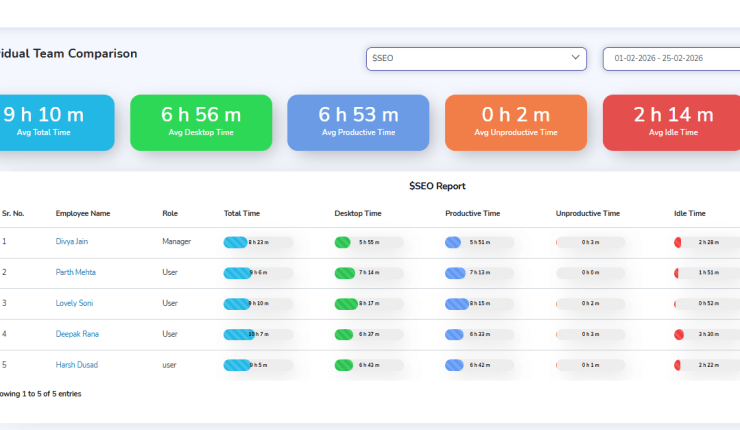
DeskTrack acts dual as a time tracking software and employee attendance management software. Implementing the tool automates time tracking so that you focus on important work. Combined with its real-time attendance tracking feature, the software ensures that employees only get paid for the days they show up to work.
| Most Affordable Paid Plan | User Rating |
| $5.99/user/month | 5/5 |
2. Buddy Punch
Buddy Punch is an attendance tracking software with useful time tracking features for SMEs. Plus, its intuitive scheduling and payroll functionalities also come in handy. Overall, this time clock software is a decent start in the world of employee hours regulation and automation for businesses.
| Most Affordable Paid Plan | User Rating |
| $4.49/user/month + $19 Monthly Base Fee | 4.8/5 |
3. Clockify

Clockify is an easy-to-use web time tracking software with a paid automatic time tracker functionality. This helps small businesses a lot in accruing work hours, logging, and efficiently calculating payroll and overtime.
| Most Affordable Paid Plan | User Rating |
| $5.49/user/month | 4.8/5 |
4. Rize
Rize is a simple AI-powered time tracking software, which is quite affordable for SMEs and small businesses. There is a unique feature of this tool called focus music, which lets employees concentrate on work while the software calculates hours.
| Most Affordable Paid Plan | User Rating |
| $12.99/month | 4.5/5 |
Final Tip to Manage Overtime Efficiently
Now, all you need is one final tip to efficiently manage and calculate overtime. We strongly suggest you use DeskTrack’s time tracking and employee monitoring software. Implementing the tool not only ensures accrued overtime pay, but also assures that the employee (s) didn’t rip you off by not working during those additional hours. Overall, whether it’s insider threats, sincere employees, overtime employees, average teams, or workers who are slacking off, DeskTrack keeps track of everyone and everything.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q. What are the Benefits of Accurate Overtime Calculation?
Ans. Here are the advantages that we experienced.
- Increased employee satisfaction
- Decreased turnover rates
- Reduced expenses
Q. How Do I Calculate My Overtime?
Ans. Here are the steps you need.
- Overtime rate is at least 1.5 times for every hour an employee works over the standard FLSA 40 hours/week. However, it can also be any amount based on the contract. For example, 1.75 times.
- Sticking to 1.5, let’s say X worked 2 hours over 40 at $10/hour. Their regular weekly pay will be: $10/hour * 40 = $400. Similarly, the overtime pay will be: $10/hour * 1.5 = $15/hour
- For overtime pay, we will simply multiply the overtime rate by their overtime hours: $15/hour * 2 = $30.
- So, their total payment for the week will be: $30 + $400 = $430.
Q. What is the Formula for Calculating Overtime?
Ans. Here are the general formulas for calculating overtime pay at a minimum of 1.5 times the regular pay rate.
- Regular Pay Rate * 1.5 = Overtime Pay Rate
- For example: $10/hour *1.5 = $15/hour
- Overtime Pay Rate * Overtime Hours = Total Overtime Pay
- For example: $15/hour * 2 hours = $30