Managing simple or complex projects shouldn’t be a mess. It’s never a smooth sail and will never be, but at least we must be properly prepared, like having all the necessary ingredients and a clear understanding of the cooking process. That’s where the critical path method plays an essential role.
CPM is a systematic technique to manage projects by identifying and sequencing key tasks. Overall, it helps you improve how you manage your projects. This approach strikes a miracle when it comes to risk management, resource prioritization, and schedule optimization. However, it can get a little tricky to wrap your head around it.
That’s where we come in to explain it as simply as possible with a real-life example. We are certain that you are going to get a lot from today’s guide. With that out of our way, we have a lot to cover, so let’s get started right away with finding your critical path method.
What is the Critical Path Method?
CPM in project management shows the longest sequence of dependent tasks and estimates the project’s minimum finish time. We recommend you apply it to complex projects because it helps you:
- Determine the earliest start and finish dates for each task.
- Spot critical dependencies between activities.
- Effectively prioritize resource distribution.
- Systematically monitor project progress.
The Importance of the Critical Path Method in Project Management
The critical path method in project management makes a systematic framework that identifies and sequences key tasks. Remember that these tasks directly influence your whole project’s completion timeline.
Basically, CPM maps out dependencies between activities, assisting you in determining the tasks that have 0 float time. Such chunks must be finished on schedule to avoid project delays.
This approach calculates the longest possible continuous path from the start to finish, considering the duration of each one and its bond with other activities.
| Expert Tip |
| 0 float time equals having no time between activities and tasks. |
Read Also: Top 11 Workflow Apps for Every Business Process in 2025
Why You Need to Use the Critical Path Method
Project managers, such as you and me, use the critical path method because of its systematic approach to streamlining timelines and organizing tasks:
- Use this approach when your desk is piled up with projects with multiple interdependent tasks.
- Forward and backward pass calculations ensure accurate timeline planning.
- It assists you in optimizing operations by breaking down complex objectives into manageable components while maintaining a transparent and visible order of activities.
Benefits of Using the Critical Path Method
Make your workday more productive
Time tracking and work management can help you reach your goals
faster.
Let’s get straight to the benefits of the critical path in project management without all the long and boring introductions that ease into it.
- CPM prioritizes critical activities while efficiently managing non-critical tasks.
- It spots potential obstructions and obstacles and calculates scheduling flexibility.
- The method enhances team communication via visual tools and transparent delegation.
- This approach streamlines resource allocation and effectively tracks project costs.
When is the Right Time to Apply CPM?
You must implement the critical path method in situations calling for very precise timeline control and resource optimization. Usually, those scenarios include:
- A multitude of interdependent tasks.
- Tight deadlines
- Complex resource management requirements.
CPM is specifically effective when it comes to managing large-scale, complex projects that need careful monitoring and risk avoidance.
How to Implement the Critical Path Method?
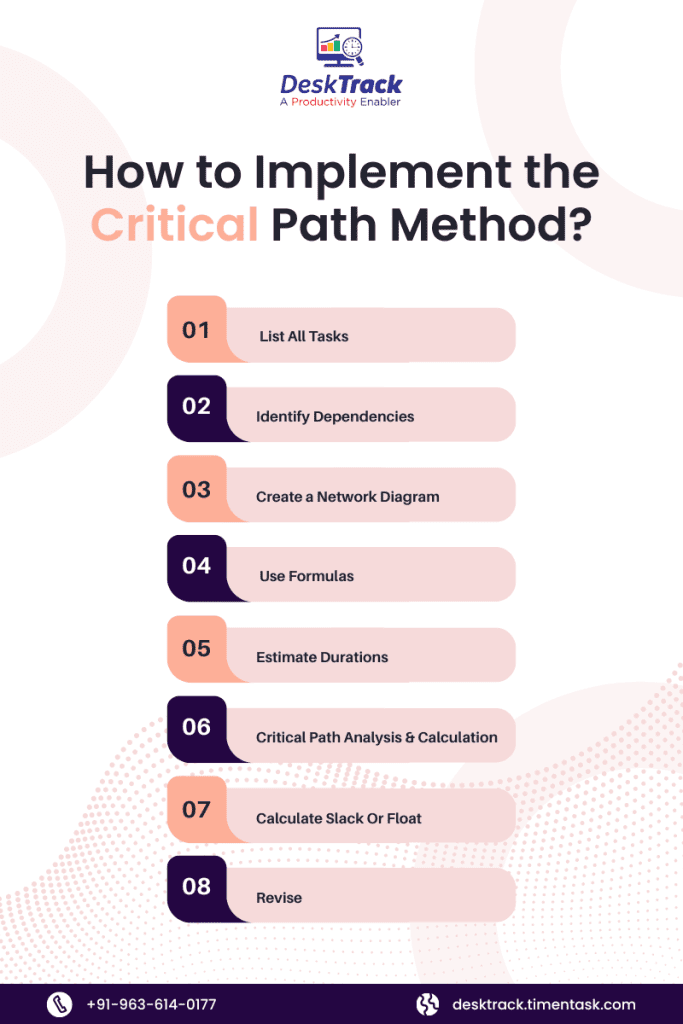
As complex as it may seem, implementing the CPM for project management is very simple as long as you are aware of the proper sequence. Below, we will break down the 8 steps to get you started:
1. List All Tasks
You need to jot down all the tasks as bullets, including every project activity from start to finish. During this step, you will need to:
- Break down critical activities into manageable components.
- Document transparent descriptions and expectations
- Establish realistic time estimates
- Make the tasks interdependent and spot predecessor bonds.
2. Identify Dependencies
Estimate the duration of each task and identify which ones you require completing before starting others. Using historical data and gathering feedback from your teams is very useful here. Overall, you must end up with a detailed dependency list that marks preceding tasks.
3. Create a Network Diagram
To track task dependencies, of course. The critical path diagram for project management is your roadmap for implementation. Simply put, you require visualizing your project’s tasks and dependencies in a detailed flowchart. Here, you must:
- Draw nodes to spot your project’s start and finish points.
- Use arrows to represent interdependencies.
- Don’t forget to include duration estimates.
- You may also need to add dummy activities in case you need to represent logical bonds.
4. Use Formulas
Now we need to use the critical path formulas to obtain the earliest start (ES), latest start (LS), earliest finish (EF), and latest finish (LF) values for each task:
|
|
|
|
5. Estimate Durations
For step 4, you will also need the estimated duration of each task. For the same, break down each task into measurable units. Considering expert opinions, resource availability, potential risks, task interdependency, and historical data, here is a wise choice. Now, all that’s left for you to do is make contingency plans for highly uncertain activities.
6. Critical Path Analysis & Calculation
To manually calculate the project management critical path, you will require working through both the forward and backward path calculations. However, what are those? Simply put, the forward pass estimates each activity’s earliest start and finish, while the backward formula is for getting each task’s latest start and finish. Once done, you can spot the critical path, which is the sequence of tasks with 0 float.
7. Calculate Slack Or Float
You need to take into account the total and free float while calculating slack in the project schedule. Wrapping your head around these two values is essential to making informed decisions regarding the scheduling of tasks:
- Total float is the maximum delay permitted without affecting the end of the project.
- A free slack signals the available delay time without affecting the next activities.
- The total float is for the entire project.
- Free float is particular to individual tasks.
8. Revise
During the project execution phase. Obviously. Since no project is certain, and any circumstances can cause delays or extend the task duration, it is a wise idea to continue updating the critical path diagram.
How to Apply CPM in Project Management?

Applying the critical path method in project management just takes 3 steps. So, it’s not that time-consuming. All you have to do is use schedule compression techniques, resolve resource conflicts, and collect data for future projects:
1. Schedule Compression Techniques
These assist in overcoming timeline challenges, as they provide you with practical solutions to decrease duration without compromising scope. The top approaches here are:
- Fast-Tracking: Running activities in parallel, whenever possible.
- Crashing: Adding resources to speed up critical path tasks.
- Hybrid: Combining both the above methods.
- Resource Optimization: Balancing cost against time savings carefully.
2. Resolve Resource Constraints
3 elements in critical path project management determine successful resource constraint management, including identification, analysis, and resolution. So, to maintain project timelines while streamlining resource spending, resource levelling and smoothing techniques are very useful.
3. Data Collection
For future projects. Of course. Regardless of CPM, tracking and saving project data for decision-making for upcoming projects is a strong suggestion. Below, we have listed the data you need.
- Historical task durations and dependencies
- Resource utilization patterns
- Critical path variations
- Cost performance metrics
Critical Path Method Vs. Other Techniques
There are other approaches as well, such as PERT and Gantt charts with their own limitations, pros, and applications, just like the critical path method:
| Feature | CPM | PERT | Gantt |
| Primary purpose | Grab the largest road of dependent tasks to determine the project duration | Estimate project duration under uncertainty | Visually map timelines and tasks |
| Time estimation | Fixed (deterministic) durations | 3 estimates, including optimistic, most likely, and pessimistic | Task durations shown as fixed bars |
| Best for | Projects with predictable timelines | Projects with uncertain durations | Any project requiring visual tracking |
| Handles uncertainty | No | Yes | No |
| Focus | Critical tasks that determine the project’s end date | Probabilistic outcomes and flexibility | Progress tracking and timeline visibility |
| Shows task dependencies | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Ease of use for terms | Moderate | Moderate | High |
| Supports visual progress tracking | Limited | Limited | Yes |
Read Also: How To Calculate Full Time Equivalent (FTE) Accurately?
CPM Challenges You Need to Immediately Address

Despite its well-known use, CPM project management has several limitations that can impact how you plan and execute projects. Although it is great for providing a structured approach to scheduling, it lacks what’s necessary for real-world, fast-moving atmospheres, where plans are just for show and tell:
1. Limited Flexibility in Handling Unexpected Events
CPM is based on fixed task sequences and durations. The assumption here is that once the plan has been drafted, execution will be straightforward with little to no deviation. However, we all know that unexpected delays are common. Remember that any change in the critical task affects the entire timeline. So, if you are not regularly updating your diagram, the entire project is done for.
The Solution: Use the right project management software solution for real-time adjustments and automatic critical path recalculations.
2. Complex Diagrams are Hard to Communicate
The critical path project management diagram grows more complex with the gradual increase in tasks. If your teams and stakeholders are not trained in it, they may ignore or find the flowchart confusing. This is not what we want.
The Solution: Distribute large projects as sub-projects with their own mini critical paths.
3. Insufficient Focus on Resource Allocation
The tools, human resources, and budget required are ignored. Simply put, tasks may appear correctly scheduled. However, you may not have enough teams at the right time. In layman’s terms, we can say that objects in the mirror are closer than they appear.
The Solution: Combine CPM with resource levelling and workload management software.
4. Inaccurate Task Duration Estimations
The project duration here is fully based on best guesses and positive assumptions. However, we all know that many circumstances can extend or shorten a task’s duration in real life.
The Solution: Use historical project data and estimation methods to get more realistic timelines and project assessments.
Real-Life Example of Critical Path Method
A good part about the critical path method is that it can be applied in any situation. This example of throwing a party, or you can say party planning and execution, will give you a better understanding:
1. Define the Scope
First, you need to collect a list of tasks that you need to execute to throw your party. For instance, selecting a venue and date. You should also figure out task dependencies, for example, inviting your so-called friends is dependent on selecting a date and venue.
| Task | Dependency |
| Select a date and venue | N/A |
| Create a song playlist | N/A |
| Get the sound system ready | N/A |
| Invite your so-called friends | Select a date and venue |
| Buy the food and drinks | Invite your so-called friends |
| Prepare your famous tomato sandwiches | Buy the food and drinks |
| Host the party | Sound system and tomato sandwiches |
2. Define the Different Project Paths
It’s normal to have multiple critical paths running concurrently in this project. This can be due to multiple dependencies or separate sequences having the same duration. For example, one path can be for booking the venue, which involves:
- Browsing various options
- Visiting potentials
- Finalizing the booking
You get the idea. Right?
3. Consider the Resource Restrictions
According to our example, it’s impossible to prepare the tomato sandwiches without bread and tomatoes. Similarly, if you are working in teams, you can split the tasks between your so-called friends. For instance, while you are busy booking the venue, your friends can arrange for food, drinks, and music. However, if you are the only one doing all the arrangements, considering the resource restraints is important.
4. Calculate Project Length
Now, in our example party CPM, we need to calculate the time needed to complete each of our tasks. To make it clear, we have included the duration in hours. Plus, we have assumed the start to be ES.
| Task | Duration (In Hours | Start |
| Select a date and venue | 2 | Monday |
| Create a song playlist | 3 | Monday |
| Get the sound system ready | 1 | Monday |
| Invite your so-called friends | 48 | Monday |
| Buy the food and drinks | 24 | Tuesday |
| Prepare your famous tomato sandwiches | 2 | Wednesday |
| Host the party | 2 | Wednesday |
5. Leave Space for Flexibility
Of course, circumstances such as rain or laziness can affect how much time it takes for you to arrange the party. So, leaving room for flexibility is a great idea here.
6. Adjust to the Changes
Now, all you need to do is adjust to the changes as the circumstances change for success. This is how the critical path method works in non-fiction.
7. Compress the Schedule (If Required)
In case some of the task durations, such as inviting the friends, buying food and drinks, and preparing your famous tomato sandwiches, are shortened, you will be required to reschedule accordingly. That’s because if one task duration is shorter than the estimate, you get more time for other tasks.
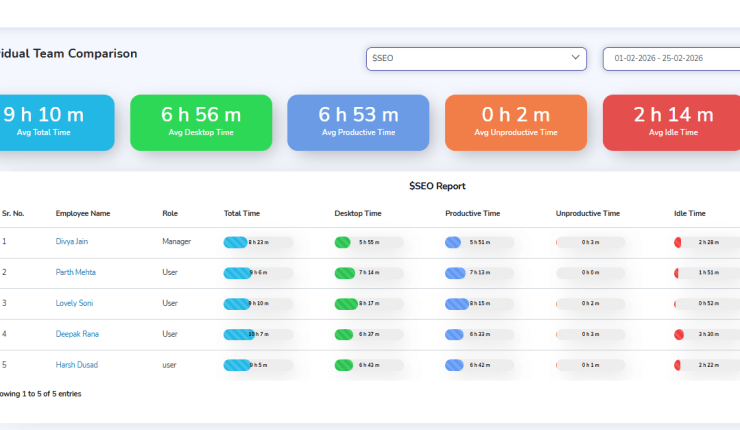
Why is DeskTrack the Best Project Management Software?
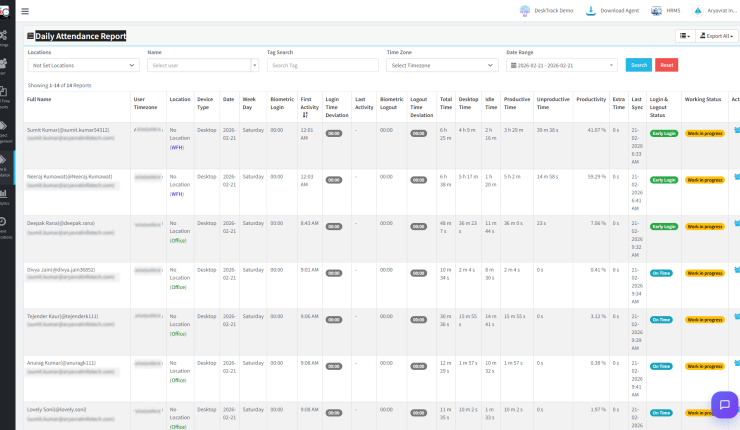
Using the project management software, DeskTrack, you can implement the critical path method more easily. It lets you subdivide the work into as many workspaces, lists, workflows, projects, tasks, checklists, and subtasks as required. Update insights in real-time and move tasks from one workflow to another within seconds. That’s how easy it is with the employee monitoring solution.
For workforce management, the attendance management feature provides you with real-time insights to ensure that you never run out of human resources. So, manage projects, monitor employees, track time, and take charge of your team’s accountability and responsibility with the most flexible software for your in-office, remote, hybrid, and field staff.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q. What is the Critical Path Method?
Ans. CPM in project management signals the longest sequence of dependent tasks and estimates the project’s minimum completion time.
Q. When is the Right Time to Apply CPM?
Ans. You must implement the critical path method in situations calling for very precise timeline control and resource optimization. Usually, those scenarios include a multitude of interdependent tasks, tight deadlines, and complex resource management requirements. CPM is specifically effective when it comes to managing large-scale, complex projects that need careful monitoring and risk avoidance.
Q. How to Implement the Critical Path Method?
Ans. You will need 8 steps:
- List All Tasks
- Identify Dependencies
- Create a Network Diagram
- Use Formulas
- Estimate Durations
- Critical Path Analysis & Calculation
- Calculate Slack Or Float
- Revise
Q. How to Apply CPM in Project Management?
Ans. You only need these 3 steps:
- Schedule Compression Techniques
- Resolve Resource Constraints
- Data Collection
Q. What are the CPM Challenges You Need to Immediately Address?
Ans. These 4 challenges are due to the fact that using CPM alone fails in real-life situations.
- Limited Flexibility in Handling Unexpected Events
- Complex Diagrams are Hard to Communicate
- Insufficient Focus on Resource Allocation
- Inaccurate Task Duration Estimations