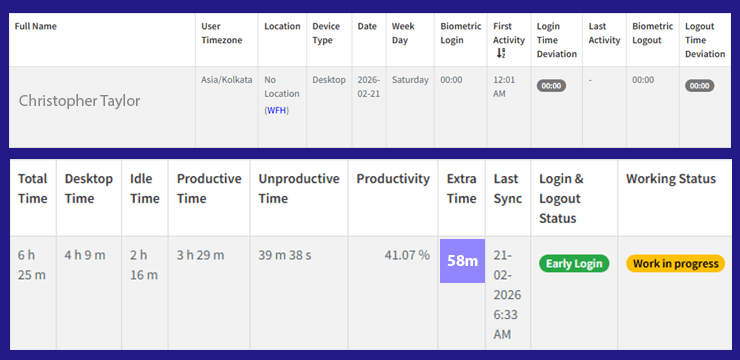
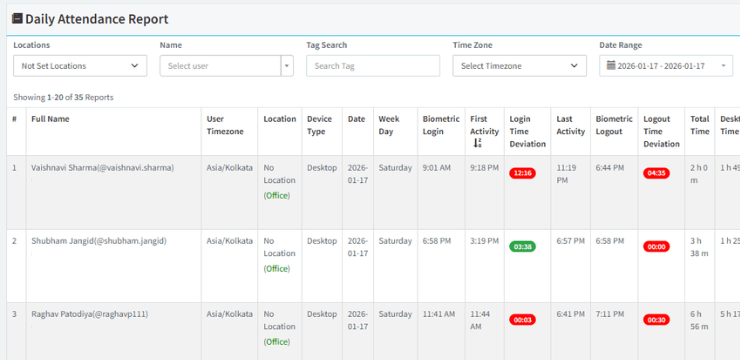
Whenever the words employment, employers, and employees come to mind, we usually think of the 9-to-5 work commitment with weekly, yearly, or monthly pay with bonuses. However, that’s only from the perspective of an individual student or employee. From a business’s perspective, there are various types of employment with varying work hours, payment types, and requirements.
Whether you have a new business or want to know what your experience will be like as a particular employee, knowing all about the types of work can get complicated. Don’t panic, we are here to help with the most common 22 categories of employees existing in today’s work world.
The 22 Types of Employment with Key Details
Before hiring someone or getting hired, knowing about the different employment types can help you decide who will fill your requirements, how much the expense will be, and a lot more. In short, it helps you make a wise choice regarding your RoI vs Costs in the long run.
1. Apprenticeship
Simply put, this structured training program offers hands-on experience and technical skills under the guidance of experienced professionals.
- Employment Period: 1-6 years
- Working Hours: 35-40 hours per week
- Salary Format: Hourly
- Benefits: May receive benefits equivalent to full-time
- Deductions & Taxes: A year-end W-2 form, standard taxes and deductions, social security, and medical contributions.
- When to Offer: When you need highly skilled workers in specialized trades, create a strong talent funnel, or prioritize long-term workforce retention and development.
Read More: Top 15 Construction Project Management Software in 2025
2. At-Will Agreement
Did you know that it’s the most common type of employment in America, with 49 out of 50 states allowing it? What makes this one interesting is that the employee or employer can terminate the contract with or without notice, for any reason, and at any time. However, the employees still get the advantage that they can’t be unlawfully discontinued.
- Employment Period: Indefinite until terminated by either party.
- Working Hours: Full-time but may vary by role and business policies
- Salary Format: Fixed or per hour. However, it may also include bonuses, commissions, etc.
- Benefits: Vary by policies
- Deductions & Taxes: A year-end W-2 form, standard taxes and deductions, social security, and medicare contributions.
- When to Offer: When you want to maintain flexibility at both the business and employee end.
3. Casual
This one is a flexible work setup that involves hiring workers on an as-needed basis without the guarantee of regular work hours.
- Employment Period: Short-term
- Working Hours: Depends on your requirements
- Salary Format: Hourly or one-time flat fee.
- Benefits: Limited
- Deductions & Taxes: Standard taxes and deductions, social security, year-end W-2 form, and medicare contributions.
- When to Offer: If you face fluctuating workloads, seasonal requirements, or want to decrease fixed labor expenses.
4. Commission-Based
It is one of the employment types where employees primarily get compensation based on the sales or revenue they generate.
- Employment Period: Indefinite until either party terminates it.
- Working Hours: Vary by designation and business policies
- Salary Format: A fixed percentage of sales, a flat fee per sale, or a mix of both.
- Benefits: Health insurance, PTO, and retirement plans.
- Deductions & Taxes: Social security, standard taxes and deductions, medicare contributions, and year-end W-2 form.
- When to Offer: for sales roles and incentivizing high performance.
5. Consulting
A consultant is a self-employed professional. These people usually provide clients with expert advice or services on a per-project basis.
- Employment Period: Project and engagement-based
- Working Hours: Flexible
- Salary Format: Hourly rate or flat fee
- Benefits: Self-determined
- Deductions & Taxes: Yearly self-employment and estimated taxes. Plus, a year-end 1099-MISC form (client end)
- When to Offer: Whenever you need specialized expertise without incurring long-term employment expenses.
6. Independent Contractor
These are also self-employed people who provide clients with expert advice and services based on contracts. However, what makes them different from consultants is that independent contractors usually engage in structured, longer-term contracts.
- Employment Period: Contract-based
- Working Hours: Flexible. However, contractors working with full-time workers may require maintaining regular office hours.
- Salary Format: A flat fee or hourly rates
- Benefits: Self-determined.
- Deductions & Taxes: Yearly self-employment and estimated tax with a client-end 1099-MISC form.
- When to Offer: If you only have short-term specialized projects not need any full-time dedication.
7. Fixed Term Contract
This work type involves a predetermined start and end date.
- Employment Period: A few months to several years
- Working Hours: 40 weekly hours. However, it may vary according to project needs.
- Salary Format: Fixed or hourly
- Benefits: Depends on the employer
- Deductions & Taxes: Same as full-time
- When to Offer: If you prioritize workforce flexibility, project-based requirement management, and evaluating potential hires.
Make your workday more productive
Time tracking and work management can help you reach your goals
faster.
8. Freelancing
Freelancers are again self-employed individuals, working independently. They usually offer short-term, per-project-based services.
- Employment Period: Contract or project-based
- Working Hours: Flexible
- Salary Format: A flat fee, hourly rate, or commission. This depends on the terms and conditions of the contract.
- Benefits: Self-determined
- Deductions & Taxes: Yearly self-employment and estimated taxes with a year-end 1099-MISC form from the client side
- When to Offer: When you have short-term projects requiring irregular specialized skills.
9. Full-Time
As a full-time employer, your employees will usually work exclusively for you. Plus, you can also forbid them from working for other clients, businesses, or freelancing by stating it in the employment contract. However, you will not be this harsh. Will you?
- Employment Period: Indefinite
- Working Hours: A consistent schedule with the hours depending on the sector and designation.
- Salary Format: Hourly wages or fixed salaries.
- Benefits: Health insurance, PTO, retirement plans, and other perks.
- Deductions & Taxes: Standard deductions and taxes, social security, medicare contributions, and a year-end W-2 form.
- When to Offer: When you need core roles with consistent and long-term commitment
10. Internship
In simple terms, an internship is a temporary position that lets younger individuals get practical experience as well as learn new skills.
- Employment Period: Specific duration
- Working Hours: Varies but is usually part-time or full-time.
- Salary Format: Stipend, fixed, or hourly
- Benefits: Not legally required for businesses to provide benefits to interns.
- Deductions & Taxes: Under particular American conditions, interns are the same as W-2 employees under FLSA, entitled to overtime pay and minimum wage.
- When to Offer: When you want to enhance employee branding, create a funnel of high-potential individuals aligned with your values, and attract and grow young talent.
11. Leased
This type of employment involves businesses contracting with third-party staffing agencies to hire talent, where the agency acts as an EoR to handle payroll, benefits, and HR functions. A variation of this is insourcing and offshoring.
- Employment Period: Depends on your needs, employee skills, and availability.
- Working Hours: Typically full-time. However, you can make adjustments to meet your organization or project’s requirements.
- Salary Format: Usually per hour. However, some might receive a fixed salary.
- Benefits: Employees might get benefits.
- Deductions & Taxes: Standard deductions and taxes, and a year-end W-2 form.
- When to Offer: When you must fill temporary designations fast, scale your workforce, access particular skills without full-time, or outsource specific functions.
12. On-Call
On-call employees are those who are called in to work as and when needed, frequently on short notice.
- Employment Period: Ongoing. However, continuous work is not guaranteed.
- Working Hours: Depends on your requirements and employee availability
- Salary Format: Usually hourly. However, they may get a monthly retainer.
- Benefits: Limited and depend on the hours worked.
- Deductions & Taxes: A year-end W-2 form with standard taxes and deductions.
- When to Offer: If you are facing unpredictable workloads, surprise absences, or peak demand periods.
13. Part-Time
Like full-time workers, part-time employees also work on a fixed schedule. However, their work hours or days are fewer.
- Employment Period: Ongoing or temporary
- Working Hours: 20-30 weekly hours
- Salary Format: Hourly
- Benefits: Limited and depend on your policies and the number of hours worked.
- Deductions & Taxes: A year-end W-2 form with standard deductions and taxes.
- When to Offer: If you must cover particular shifts or the workloads fluctuate a lot.
14. Probationary
This employment type is what we know as a trial period at the beginning of a new job, in layman’s terms. What it does is let employers evaluate a new hire’s skill, performance, and cultural fit.
- Employment Period: 30-90 days. However, it can be longer or shorter depending on the designation and your policies.
- Working Hours: Full-time
- Salary Format: Same as full-time
- Benefits: Limited, depending on probation length and your policy.
- Deductions & Taxes: A year-end W-2 form and standard deductions and taxes.
- When to Offer: When you want to enhance your hiring results.
15. Seasonal

Seasonal workers are a good fit for filling staff shortages during specific periods, such as holiday seasons. This is one of the different types of employment where employees are hired for a specific time bracket to meet increased product and service demands.
- Employment Period: Industry and designation-based variations.
- Working Hours: Part-time to full-time, frequently with fluctuating schedules to account for peak demand brackets.
- Salary Format: Hourly with potential overtime pay. However, employees might also receive a per-piece rate depending on the number of units manufactured or harvested.
- Benefits: Limited due to seasonal workers being considered temporary.
- Deductions & Taxes: Year-end W-2 form with standard taxes and deductions.
- When to Offer: If your business gets cyclical demands a lot. For example, retail during holidays.
16. Self
If you are one of those people who are earning money without a traditional employer-employee bond, then you will fall under the self-employment category.
- Employment Period: Indefinite
- Working Hours: Flexible. It depends on your business and financial requirements, and work ethic.
- Salary Format: Revenue generated – expenses
- Benefits: Self-determined.
- Deductions & Taxes: Self-employment and quarterly taxes.
- When to Offer: If you are on good terms with ex-employees who are now self-employed and would like them to take assignments on an ad-hoc or retainer basis.
17. Temporary
Temporary employment is the type of employment where you hire workers for a particular period. This is typically a great option to fill in for absent employees, finish short-term projects, or meet temporary workload upshifts.
- Employment Period: A few days to several months
- Working Hours: Part-time to full-time based on the assignment.
- Salary Format: Hourly with potential overtime pay.
- Benefits: Limited or minimal benefits.
- Deductions & Taxes: A year-end W-2 form and standard deductions and taxes.
- When to Offer: When you have short-term staffing requirements.
18. Temp-to-Perm
Initially, you will hire employees temporarily. However, if you spot potential in them, the business need arises, or if they perform well, you will transit them to permanent designations.
- Employment Period: The start is temporary, with the potential to become permanent
- Working Hours: Part-time to full-time
- Salary Format: Hourly with potential for overtime pay (when temporary). Salaried or hourly (when permanent)
- Benefits: Limited (when temporary). Full-time benefits (when permanent)
- Deductions & Taxes: A year-end W-2 form with standard taxes and deductions.
- When to Offer: When you need long-term staffing but want to evaluate the performance and culture fit of the candidates before taking a permanent hiring step.
19. Tenured
This one is usually accustomed to the education industry. This is where individuals, including university professors, get job security due to indefinite employment.
- Employment Period: Long-term, frequently lasting till retirement.
- Working Hours: A set number of weekly teaching hours with other responsibilities.
- Salary Format: Fixed annual salary with additional compensation.
- Benefits: Comprehensive salary packages with retirement plans, PTO, and health insurance
- Deductions & Taxes: Medicare contributions, social security, standard taxes and deductions, and a year-end W-2 form.
- When to Offer: Provide to faculty members with teaching, research, and service excellence, who are considered essential to your institution’s long-term objectives.
20. Traineeship
This one is a structured training program that aims to equip individuals with the particular knowledge and skills they need for a certain industry or job.
- Employment Period: A few weeks to several months
- Working Hours: 40 weekly hours. However, it might vary based on the employer and program.
- Salary Format: Low salary or stipend
- Benefits: Limited
- Deductions & Taxes: Standard taxes and deductions. However, it can also change depending on the particular terms of the traineeship you are offering and the individual’s tax status.
- When to Offer: When you want to grow a skilled workforce. This type of employment is handy if your business is in an industry with high turnover rates or requires specialized skills.
21. Volunteering
In simple terms, volunteers work for free and at their own will. These individuals work at NGOs and other not-for-profit businesses.
- Employment Period: A few hours to several years
- Working Hours: Flexible, based on business requirements and the volunteer’s availability.
- Salary Format: No salary or wages.
- Benefits: Networking opportunities, training, experience, etc.
- Deductions & Taxes: N/A
- When to Offer: If you work at a non-profit business or one with a non-profit arm, and wish to make community relationships.
22. Contingent
Want to save on benefits, long-term commitments, and administrative overhead expenses? Then, this type of employment is right for you. Contingent employees range from freelancers to temporary ones, having full control over the delivery of their work and tax filing.
Read Also: All You Need to Know About the Sandwich Leave Policy
Steps to Choose the Right Employment Type for Your Business

So, now you know about the different types of employment, you must be eager to start hiring. However, wait. You also need to consider a few more things, including:
- Legal Compliance: It is essential to understand the different types of employment to correctly classify your workforce. That is, unless you want to face expensive legal consequences.
- Cost Management: Streamline your workforce strategy by calculating and managing employment costs. It’s crucial to scale the RoI against these expenses. For example, full-time staffing comes with fixed costs, while part-time staffing is flexible.
- Loyalty Vs. Flexibility: Full-time employment comes with higher stability and loyalty, but with limited flexibility. However, temporary or contract workers are flexible without the commitment.
- Tax Implications: Understanding the different tax implications of the employment categories is also critical for precise tax reporting and regulatory compliance.
- Strategic Workforce Planning: We strongly suggest considering your long-term workforce requirements. Plus, it is also critical to account for how different employment categories can add to growing your talent pool, boosting your hiring success, and providing for your business’s overall strategy.
How Can DeskTrack Help?
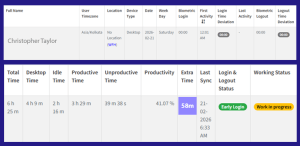
DeskTrack’s HR management feature makes the hiring and onboarding process streamlined and faster for any type of employment or employees you are looking for. Simply fill a user-friendly form and post to 100+ job boards within seconds. Your HR can track applicants, application status, and other related data in real-time to save time, reduce complexity, and decrease expenses. However, the tool provides more than this functionality. After the employee is part of the team, use the project management, screenshot monitoring, time tracking, and app, URL, and file usage tracking features to ensure that the new hire is efficient and productive as per your standards. Try now and realize why 100000 users across the globe trust DeskTrack.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q. What are the 4 Types of Work?
Ans. In a typical scenario, you can face any of these types of work on a workday (s).
- Business projects
- Internal projects
- Changes
- Unplanned work
Q. What are the Types of Employment?
Ans. There are various categories of employment, out of which we have shortlisted the top 22 most common types for you.
- Apprenticeship
- At-Will Agreement
- Casual
- Commission-Based
- Consulting
- Independent Contractor
- Fixed Term Contract
- Freelancing
- Full-Time
- Internship
- Leased
- On-Call
- Part-Time
- Probationary
- Seasonal
- Self
- Temporary
- Temp-to-Perm
- Tenured
- Traineeship
- Volunteering
- Contingent
Q. Which Type of Employment is There in India?
Ans. Mainly, Indian employment categories include formal and informal types. These are further divided based on work duration and arrangement, including full-time, part-time, temporary, fixed-term, casual, gig, freelance, and seasonal.
Q. What are the 4 Types of Employees?
Ans. According to their employment status, employees can be categorized as:
- Full-time
- Part-time
- Contract
- Independent contractor
Q. What are the 4 Main Types of Jobs?
Ans. Commonly, jobs are categorized as:
- Knowledge-based
- Skill-based
- Entrepreneur-based
- Freelance